Improve cardiac function by taking CoQ10 and selenium
06/25/2019 / By Stephanie Diaz

Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is quite common all over the world. In the U.S. alone, almost half of all adults suffer from some form of CVD. According to the World Health Organization, CVD is the number one cause of death globally. In 2016, around 17.9 million people died from CVD, 85 percent of which were due to heart attack and stroke. People who have hypertension and diabetes are especially at risk of CVD.
The American Heart Association identified tobacco use as the leading cause of heart disease. Contrary to public perception, there are more deaths related to heart disease because of tobacco use than lung cancer. Tobacco smoke has high levels of carbon monoxide, which affects the blood’s oxygen-carrying capacity. Moreover, nicotine in tobacco is known to increase heart rate and blood pressure.
Cardiomyopathy is a type of CVD that weakens the heart muscles. People diagnosed with cardiomyopathy are unable to pump blood to the rest of the body effectively. There are four general types of cardiomyopathy: dilated cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (ARVD), and restrictive cardiomyopathy. Cardiomyopathy, if not managed or treated, can lead to health problems such as arrhythmia, cardiac arrest, or heart valve disorders. A study published in the New England Journal of Medicine linked cardiomyopathy to tobacco use. (Related: Chinese Medicine prescription found to improve heart function in those with dilated cardiomyopathy.)
Selenium and CoQ10 can improve heart function
Research published in the International Journal of Cardiology evaluated the effect of selenium and coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) on men 70 to 88 years old who were diagnosed with cardiomyopathy. During the four-year study, 443 men were given either a combination pill of selenium and CoQ10 or a placebo. They found that men who took the combination pill improved their overall heart health and reduced their risk of dying from heart disease by 54 percent.
Selenium is a trace mineral that is essential for the maintenance of cognitive function, immune system function, and fertility of both men and women. Selenium is part of a compound called selenoprotein. Just like antioxidants, selenoprotein protects against further damage caused by free radicals. It also has anti-inflammatory properties and can prevent the deterioration of lipids and fats in the body.
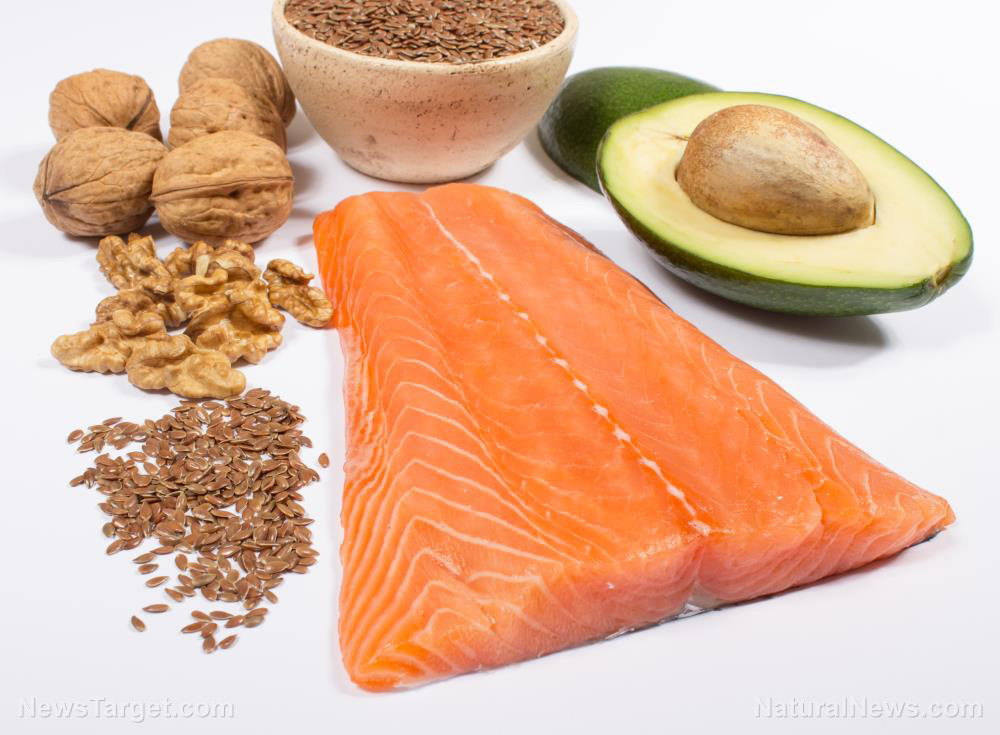
Selenium can naturally be found in food. The best sources of selenium include Brazil nuts, fish, brown rice, and eggs.
CoQ10 is a substance that is essential in generating energy in cells. The body can produce CoQ10 naturally, but unfortunately, production declines with age. Deficiency in CoQ10 is linked to heart disease, brain disorders, diabetes, and cancer. Research published in the journal JACC: Heart Failure showed that patients with heart failure responded well to CoQ10 treatment. Their symptoms improved, and they reduced their risk of dying from heart problems.
While supplementation is one way to increase the intake of CoQ10, it is better to get it from natural sources. CoQ10 is abundant in fatty fish, fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts and seeds, as well as meats.
The heart is the center of the cardiovascular system. It is involved in various bodily functions, thus having a healthy heart is essential to your overall well-being. A sure way of maintaining a healthy heart is through diet and exercise, plus finding a way to incorporate CoQ10 and selenium into your diet will surely help your heart maintain proper function.
For more information on other natural compounds that keep heart disease at bay, visit SupplementsReport.com.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
alternative medicine, cardiomyopathy, cardiovascular diseases, cardiovascular health, Coenzyme Q10, CoQ10, disease treatments, food cures, heart disease, heart health, longevity, minerals, natural cures, natural medicine, nutrients, nutrition, prevention, research, selenium, stopsmoking, supplements, tobacco smoking
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
HeartDisease.News is a fact-based public education website published by Heart Disease News Features, LLC.
All content copyright © 2018 by Heart Disease News Features, LLC.
Contact Us with Tips or Corrections
All trademarks, registered trademarks and servicemarks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.